In Microsoft Office 365, managing mailboxes is a crucial task for administrators. Deleting mailboxes may seem straightforward, but understanding the differences between soft delete and force delete is essential for efficient email management, security, and recovery. In this article, we will explore both types soft and force Delete Mailbox, their processes, benefits, and when to use each one.
Table of Content
Types of Office 365 Mailbox Deletion:
As we all know, there are two ways for deletion of a mailbox: soft deletion and permanent deletion. Therefore, Let’s take a look at an overview of both soft-deleted and force-deleted mailboxes.
What is Soft Delete in Office 365?
A soft delete refers to the removal of a mailbox from the active directory, but it is still retained in a recoverable state for a certain period. This process ensures that the mailbox can be restored if necessary, providing a safety net for accidental deletions or mistakes.
When a user is removed from Microsoft 365 or Exchange Online, their mailbox is soft deleted, but all the data is retained for 30 days by default. Although, during this period, administrators can restore the mailbox if the deletion was accidental or the account is reactivated.
Key Scenarios for Soft Delete:
- User Account Deletion: When a user is deleted in the Azure Active Directory, the associated mailbox is soft deleted.
- License Removal: Removing a Microsoft 365 license from a user results in the mailbox being soft deleted.
What is Force Delete in Office 365?
A force delete permanently removes a mailbox and its data, making it unrecoverable through normal methods. This action is typically irreversible and should be used with caution, especially in cases where sensitive information needs to be securely deleted.
Unlike soft delete, which retains the mailbox for a retention period, force delete removes the mailbox immediately and does not leave a recovery window.
Key Scenarios for Force Delete:
- End of Retention Period: Once a mailbox surpasses its 30-day retention window, it is permanently force deleted from the system.
- Manual Purging: Administrators can force delete a mailbox at any time using PowerShell.
Key Differences Between Soft Deleted and Force Deleted Mailbox
– Recovery Window
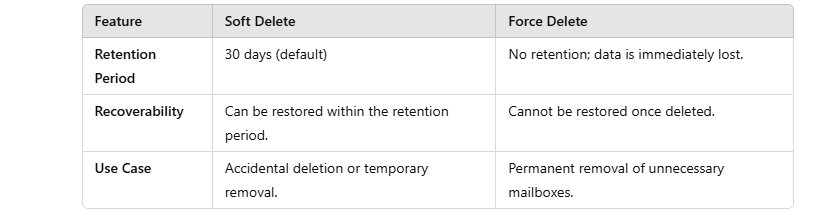
– Security and Compliance Implications
Soft deletes are a great option for data recovery and ensuring compliance with legal retention policies. Force deletes are more suited for cases where sensitive data must be securely removed, especially in industries with strict data protection regulations.
Soft and Force Delete Mailbox from Exchange Online:
Let’s explore the methods to remove a mailbox from Microsoft 365 effectively:
Soft Delete Mailboxes from Office 365
Here are the methods to soft delete Office 365 mailboxes using the Exchange Admin Center and PowerShell.
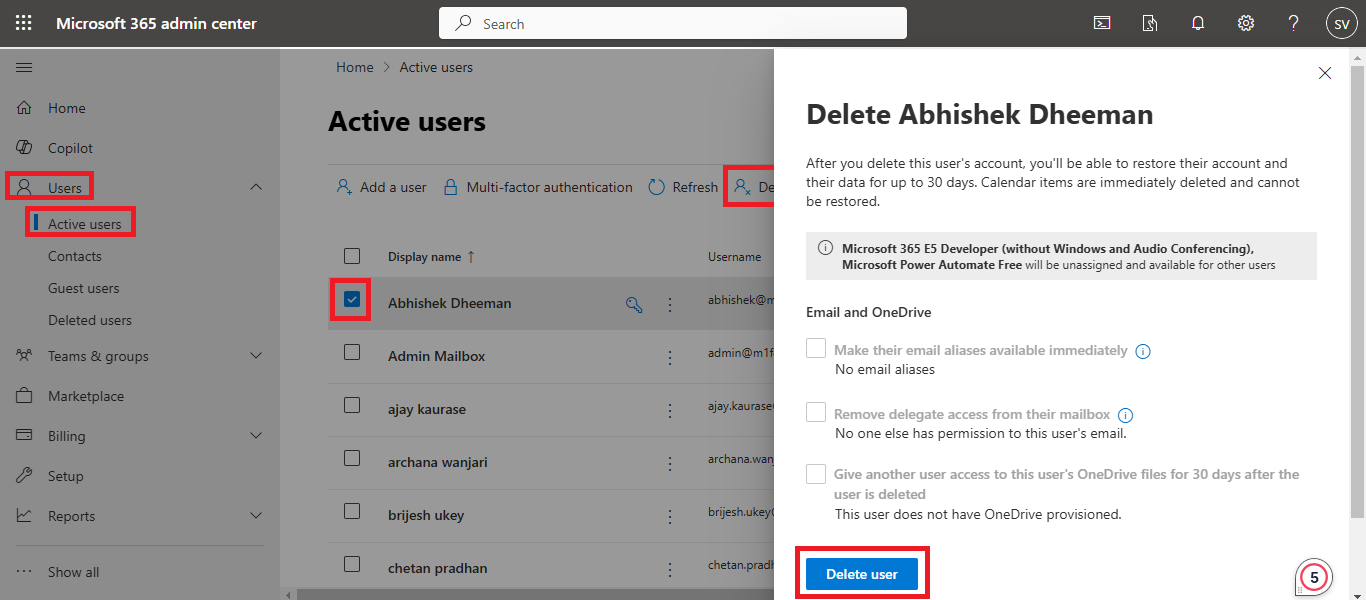
– Soft Delete a Single Mailbox Using the Office 365 Admin Center
- Visit office.com and log in with your admin credentials.
- Navigate to the Office 365 Admin Center.
- Click on Users > Active Users.
- Select the user from the list, click Delete User, and confirm to remove the user from Exchange Online.
– Delete Bulk Mailboxes Using the Exchange Online Admin Center
- Visit the Office 365 Admin Center and log in with your admin credentials.
- Navigate to Users > Active Users from the left menu.
- All active users will be displayed on the screen. Click the check box and Select the users you want to delete.
- A new window will open on the right side.
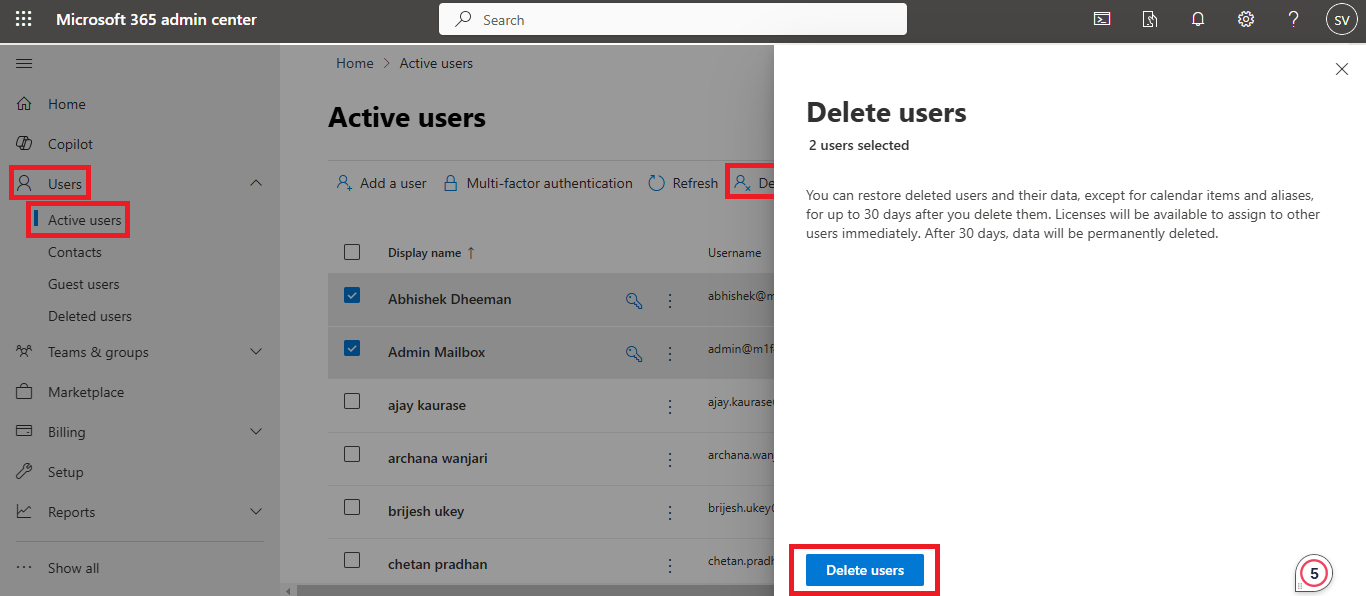
- Confirm the deletion. The number of selected mailboxes for deletion will be displayed for your review.
– Soft Delete Office 365 Mailbox Using PowerShell
After connecting to Exchange Online via PowerShell, run the following command to soft delete a user mailbox:
Remove-Mailbox –Identity <lt;MailboxAddress> -Confirm:$false
-How to Restore a Soft-Deleted Mailbox?
Soft-deleted mailboxes can be restored through the Microsoft 365 Admin Center or Exchange Online PowerShell. However, restoring through PowerShell requires running the Undo-Soft Deleted Mailbox command:
code:
Undo-SoftDeletedMailbox -Identity "[email protected]"
Force Delete Mailbox
There is no option in the Admin Center to perform a hard delete for mailboxes. You must use Windows PowerShell to force delete a mailbox.
– Force Delete Mailbox through Exchange Online PowerShell
First, open PowerShell as an administrator and connect to Exchange Online using this command:
Connect-ExchangeOnline  
– Get Soft Deleted Mailboxes in Exchange Online
To view details of all soft-deleted mailboxes, use the following command:
Get-Mailbox –SoftDeletedMailbox  
– Hard Delete a Mailbox through Exchange Online
To permanently delete a mailbox, run this command:
Remove-Mailbox –Identity <MailboxAddress> -PermanentlyDelete:$true -Confirm:$false  
– Hard Delete a Soft Deleted Mailbox Using Exchange Online Powershell
If a mailbox has been soft deleted and you want to permanently remove it, use this command:
Get-Mailbox -Identity <MailboxAddress> -SoftDeletedMailbox | Remove-Mailbox -PermanentlyDelete -Force -Confirm:$false  
By following these steps, you can easily manage and remove mailboxes in Microsoft Office 365 using both the Admin Center and Windows PowerShell.
Why Do We Need to Remove a Mailbox from Outlook Office 365?
There are several reasons to soft delete or force delete a mailbox in Office 365:
- Organizational Changes: When an employee leaves the company, their mailbox may need to be removed to manage access and maintain security.
- Storage Management: Deleting unused mailboxes helps free up storage space, ensuring resources are used efficiently.
- Security and Privacy: Removing mailboxes no longer in use minimizes security risks and protects sensitive data.
- License Optimization: Deleting inactive mailboxes allows you to reallocate licenses to active users, reducing costs.
- System Performance: Clearing unnecessary mailboxes improves system performance and simplifies maintenance for active users.
How to Manage Deleted Mailboxes Effectively in Office 365?
– Monitor Soft-Deleted Mailboxes
Admins should frequently monitor the status of soft-deleted mailboxes using the Microsoft 365 Admin Center. Tracking these deletions helps identify whether any mailboxes need to be restored before the retention period expires.
– Set Clear Retention Policies
To align with organizational needs, set clear mailbox retention policies that specify how long soft-deleted mailboxes should be retained. This ensures compliance with legal requirements and helps avoid unnecessary data loss.
– Leverage PowerShell for Management
PowerShell offers great flexibility when managing deleted mailboxes in Office 365. By familiarizing themselves with relevant commands like Undo-SoftDeletedMailbox and Remove-Mailbox, administrators can streamline their mailbox recovery and deletion processes.
Conclusion
Managing mailboxes in Microsoft Office 365 requires a careful understanding of the differences between soft delete and force delete. However, soft delete provides a recovery window for mistakenly deleted mailboxes, while force delete mailbox permanently removes them for secure data management. By knowing when and how to use each deletion method, administrators can ensure both the security and accessibility of mailbox data.













